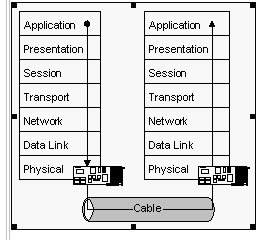
Normally a communication request originates at the highest layer (Application Layer). The request is passed down through the lower layers in the form of a packet called a protocol data unit (PDU). Layers in the protocol stack communicate with their adjacent layers via one or more Service Access Points (SAP). Each succeeding layer in the stack adds its own information to the PDU that will be read by its counterpart (peer) layer on the receiving system. Once the data arrives at the lower layers, the PDU is encoded into data frames and placed onto the cable for transmission. The data frames make their way to the receiving system and the entire process is reversed as the PDU makes its way up the protocol stack. As it moves up the stack, each layer "unwraps" the PDU and receives the information from its peer layer on the sending system.
Note that there is no by-passing of layers. Also note that it is not possible for one layer to communicate directly with its peer layer on the other system. Peer-to-peer layer communication takes place by adding messages to the PDU and sending it down through the lower layers, across the cable, and then up the stack to the peer layer on the receiving system.